Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) – a new aerosol toxicity metric and aerosol lung cell cultures studies
Epidemiological studies have shown consistently positive correlations between aerosol particle exposure and a range of adverse health effects. The World Health Organisation (WHO) lists air pollution particles as the most pressing public health issue, accounting for ca. 5% of all deaths worldwide. Despite a large number of studies on atmospheric particle toxicity, the biological pathways causing the adverse health effects of particulate air pollution are poorly understood and there is no conclusive evidence as to which particle properties are causing their toxicity. Chemical particle components are likely a key factor, but are difficult to accurately define. Identifying health-relevant particle parameters, components and ultimately sources would be crucial for improved and efficient air pollution mitigation strategies.
Atmospheric aerosol particles contain a range of oxidising aerosol components (i.e. Reactive Oxygen Species, ROS), which are potentially toxic as they can oxidise biological molecules at the liquid lung surface layer or generate oxidising components once deposited on the lung surface. From an analytical point of view it is highly challenging to quantify these oxidising particle components as some of them have short lifetimes requiring fast measurement techniques.
(1) Reactive Oxygen Species, ROS. We are developing and deploying a novel instrument to quantify ROS as a sum parameter with a technique that captures reactive and short-lived ROS components immediately after being pumped into the instrument.
This new instrument has a time resolution of about 5minutes and is sensitive enough to characterise ROS concentrations and evolution in laboratory and field experiments.

Figure 5. Photo on the portable, home-built online ROS instrument suitable for long-term field measurements.
(2) Peroxyacids synthesis. It is hypothesised that organic hydroperoxides and peroxy acids are compounds classes significantly contributing to particulate ROS. In addition, recent studies show that these two compound classes are potentially involved in atmospheric new particle formation, which is an important aspect of aerosol effects on climate.
We are synthesising and characterising atmospherically-relevant peroxy acids to obtain standards which allow unambiguous identification of these compounds in organic aerosol and to assess their atmospheric and health importance.
(3) Nanoparticle – lung cell culture online deposition chamber. We built a unique instrument which allows to deposit aerosol particles in the nm size range efficiently and evenly onto cell cultures. This process mimics accurately the in vivo physiological conditions and particle deposition in the lung. In collaboration with cell biologists and toxicologists we are investigating the effects of particle composition and particle source on the biochemical and physiological responses of lung cells.
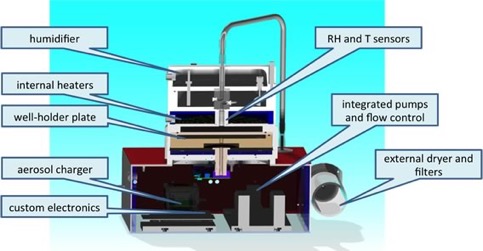
Figure 6. Nanoparticle deposition instrument to deposit particles evenly and efficiently onto cell cultures kept at physiological conditions.
Related Publications
- Fuller S.J. et al., Comparison of on-line and off-line methods to quantify reactive oxygen species (ROS) in atmospheric aerosols, Atmos. Environ., 92, 97-103, 2014.
- Platt S.M. et al., Two-stroke scooters are a dominant source of air pollution in many cities, Nature Communications, DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4749, 2014.
- Wragg F. P. H. et al., An Automated On-line Instrument to Quantify Aerosol-Bound Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) for Ambient Measurement and Health Relevant Aerosol Studies, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 9, 4891–4900, 2016.
- Steimer S.S. et al., Mass spectrometry characterization of peroxycarboxylic acids as proxies for reactive oxygen species (ROS) and highly oxygenated molecules (HOMs) in atmospheric aerosols, Anal. Chem., 89, 2873−2879, 2017.
- Mertes P. et al., A novel deposition chamber for nanoparticle – lung interaction studies, J Aerosol Medicine and Pulmonary Drug Delivery, DOI: 10.1089/jamp.2012.0985, 2013.
- Künzi L. et al., Toxicity of aged gasoline exhaust particles to normal and diseased airway epithelia, Nature Scientific Reports, 5, doi:10.1038/srep11801, 2015.
Quick Links
Social Media
