Radon-222 as relevant atmospheric tracer
Contact Dr. F. Conen L. Zimmermann
Project inserted in the frame of the ICOS-CH infrastructure (Integrated Carbon Observation System- the Swiss contribution to a European Research Infrastructure)
Cooperation: ANSTO Atmospheric Mixing (Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation)
Radon-222 is naturally emitted from land surfaces. The only sink of this noble gas in the atmosphere is radioactive decay. Its half-life of 3.8 days provides for large concentration differences between the planetary boundary layer and free tropospheric air, making it a good tracer for recent land contact of air masses sampled at the high altitude observatory Jungfraujoch. Through this project we provide daily updated radon-222 concentrations for Jungfraujoch (3454 m a.s.l.) and for Bern (575 m a.s.l.), located 60 km to the NW of Jungfraujoch. Earlier results of the project include the characterisation (mapping) of radon-222 flux in Europe, the USA and Russia.
Atmospheric radon data

daily updated radon monitor data (Bern and Jungfraujoch).
link to data source.
Collaboration
Flux maps (EU, USA, Russia)

EU annual 222Rn flux map for 2006 1°x1° resolution (fluxmaps/rn_flux_2006_1x1_atom_cm_s-1.zip)
EU annual 222Rn flux map for 2006 0.5°x0.5° resolution (fluxmaps/eu_rn_05deg.zip)
EU weekly 222Rn flux maps (fluxmaps/rn_ascii_weekly_2006.zip)
US 222Rn flux map (fluxmaps/us_rn_50km.zip)
Russian 222Rn flux map (fluxmaps/ru_rn_05deg.zip)
Details on maps and local flux time series in Szegvary 2007 and flux maps info.
Local flux time series
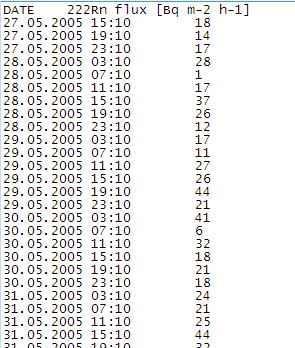
Swiss Locations:
- Aigle
- Basel/Binningen
- Oensingen
- Bern/Liebfeld
- Pully
- Robbia
- Ruenenberg
- Visp
Download data as zip (/fluxtimeseries/fluxtimeseries.zip), detailed information as pdf (fluxtimeseries.pdf)
Publications
- Radon as a tracer of atmospheric influences on traffic-related air pollution in a small inland city. [2016, link]
- Towards a Universal “Baseline” Characterisation of Air Masses for High- and Low-Altitude Observing Stations Using Radon-222. [2015, link]
- Net CO2 surface emissions at Bern, Switzerland inferred from ambient observations of CO2,δ(O2/N2), and 222Rn using a customized radon tracer inversion. [2014, link]
- Surface-to-mountaintop transport characterised by radon observations at the Jungfraujoch. [2014, link]
- Total bacterial number concentration in free tropospheric air above the Alps. [2013, link]
- Sources and Measurements of Radon and Radon Progeny Applied to Climate and Air Quality Studies. [2012, link]
- Evidence for Nearly Complete Decoupling of Very Stable Nocturnal Boundary Layer Overland. [2011, link]
- Comparison of one- and two-filter detectors for atmospheric 222Rn measurements under various meteorological conditions. [2010, link]
- Inter-comparison of different direct and indirect methods to determine radon flux from soil. [2010, link]
- European 222Rn inventory for applied atmospheric studies. [2009, link]
- Mapping terrestrial γ-dose rate in Europe based on routine monitoring data. [2007, link]
- Predicting terrestrial 222Rn flux using gamma dose rate as a proxy. [2007, link]
- Estimation of Hg0 exchange between ecosystems and the atmosphere using 222Rn and Hg0 concentration changes in the stable nocturnal boundary layer. [2005, link]
- Test of a northwards-decreasing 222Rn source term by comparison of modelled and observed atmospheric 222Rn concentrations. [2005, link]
- Latitudinal distribution of radon-222 flux from continents. [2002, link]
Quick Links
Social Media

